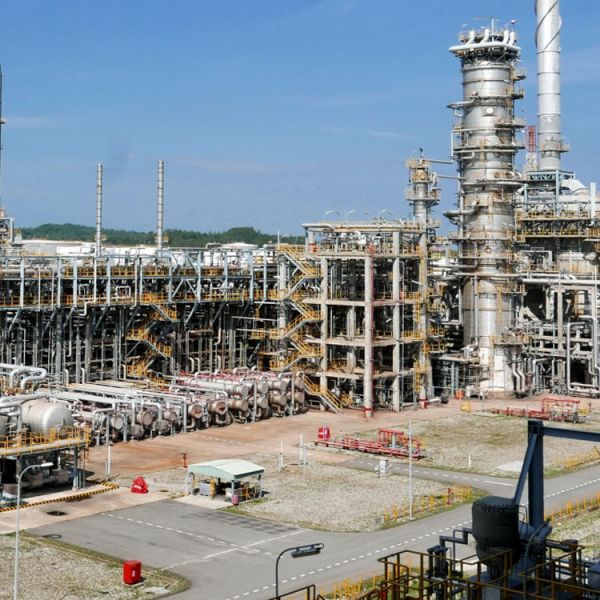
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas), also known as liquefied petroleum gas, is an important fuel source widely used in various industries, especially heavy industries such as metallurgy, building materials manufacturing, and food production.
Currently, LPG in Vietnam is sourced from two main sources: domestic production and imports. The LPG supply chain extends from upstream, midstream to downstream, encompassing extraction, processing, transportation, and bottling before reaching the point of use.
This article will help you better understand LPG quality, its impact on usage efficiency and safety, and how to choose standard-compliant LPG.
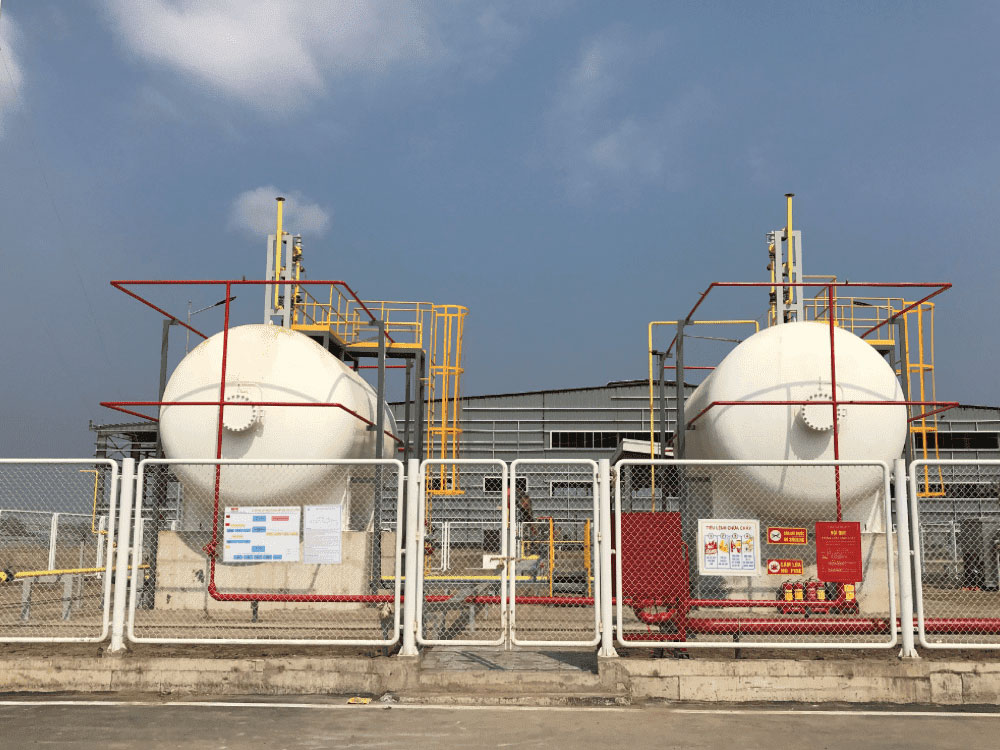

Regarding LPG supply in Vietnam
In terms of business, PV GAS has supplied nearly 2.5 million tons of LPG to the market, of which nearly 1.6 million tons were produced and consumed domestically for domestic, industrial, and transportation purposes. (According to PVGAS Annual Report 2023)
Domestic production accounts for approximately 50% of consumption:
| FACTORY | FUEL SOURCE |
| Dung Quat Refinery | Mainly from Bach Ho, Dai Hung, and other fields, and imported sources |
| Nghi Son Refinery | Imports crude oil entirely from Kuwait and the Middle East |
| Dinh Co Gas Processing Plant | From Cuu Long and Nam Con Son basins |
| Ca Mau Gas Processing Plant | Mainly from Ca Mau field and other fields |
Imports account for approximately 50% of the demand from the following markets:
Middle East (UAE, Qatar, Saudi Arabia)
South Korea, Japan
Malaysia, Indonesia
Russia, USA
What criteria are used to assess LPG quality?
LPG quality is assessed based on a Certificate of Quality issued by an independent third-party testing agency. This includes:
The origin of LPG
LPG extracted from gas processing plants typically has a higher propane content, resulting in a higher calorific value and fewer impurities, making it suitable for industrial production.
LPG extracted from oil refining processes typically has a higher butane content, making it easier to liquefy and transport, suitable for domestic use.
The main component ratio of LPG: LPG is liquefied petroleum gas consisting of 95% butane and propane. LPG typically has common propane/butane ratios such as 50/50, 60/40, and 70/30. The majority of LPG consumed on the market is commercial LPG with a propane/butane ratio of 50:50 (with a 10% margin of error).
Auxiliary components affecting LPG purity – Besides butane and propane, LPG also contains other impurities such as sulfur, water, residue, and olefins.
H₂S and sulfur compounds may appear due to chemical reactions during the processing of petroleum and natural gas.
Water (H₂O) may appear due to moisture from natural gas or crude oil that has not been completely removed during refining.
Olefins are strongly bonded hydrocarbons that often have incomplete combustion, producing residue and soot.
Note that these impurity levels must be within permissible limits for safe LPG use.
LPG Pressure – Pressure is determined by the composition of LPG. When using LPG, customers should note that pressure is always associated with temperature conditions, typically 37.8°C (100°F), similar to outdoor LPG tanks
Why is LPG quality important?
LPG quality directly impacts usage efficiency, equipment durability, and safety in production.
Higher combustion efficiency – Pure LPG ensures complete combustion, generating higher heat and reducing fuel consumption.
Protection of LPG-using equipment – Poor quality LPG can cause scale buildup on burners, soot, reduce equipment lifespan, and affect industrial combustion systems.
Ensures production efficiency and product quality – Poor quality LPG can directly impact products in certain industries such as precision molds, ceramics, electroplating, and electronic components. System maintenance can lead to production stoppages and the cost of reproducing batches.
Minimizes fire and explosion risks – Standard-quality LPG helps maintain stable pressure, reducing the risk of leaks or explosions.
Environmentally friendly – Clean LPG reduces emissions of harmful gases such as SO₂ and NOₓ, protecting the health of users..
How to identify high-quality LPG?
Check the origin of the LPG – Choose reputable LPG suppliers that provide complete LPG quality documentation and origin information when delivering to the factory.
Observe and inspect the storage system and burners – Scale buildup in the filter and burner assembly may indicate unstable LPG quality.
Observe the flame color when burning – Pure LPG burns with a consistent blue flame and no black soot. If the flame is yellow or red, the LPG may contain impurities.
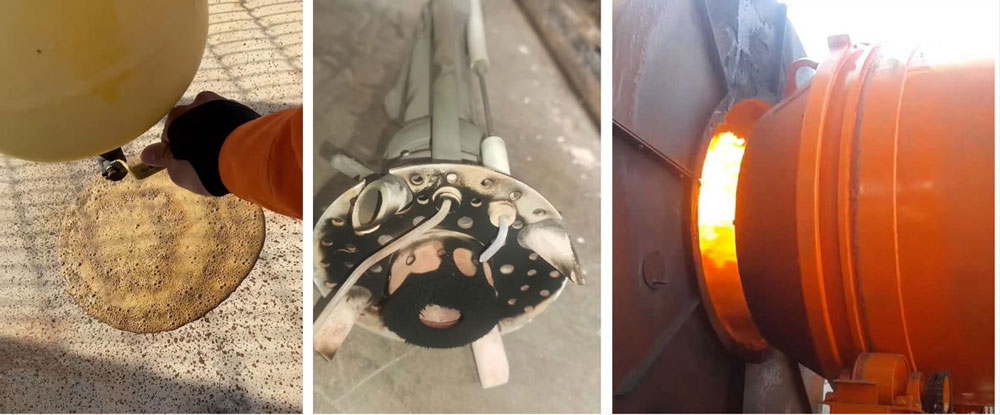

Note regarding LPG quality assessment: Observational signs are for reference only and may be due to various factors. Only authorized and specialized units have the function of testing and providing accurate conclusions.
Conclusion:
To ensure the use of standard-quality LPG, choose a reputable supplier with quality certifications and good after-sales service and maintenance. Check the origin and safety standards when purchasing LPG to save costs, protect equipment, and ensure safety during production.