Dubbed the "energy of the new era," liquefied natural gas LNG is becoming increasingly popular in many developed countries worldwide. So what exactly is LNG? What are its distinguishing features and how is it produced? Why is LNG considered an environmentally friendly fuel source and widely favored around the world? Let's explore this topic of liquefied natural gas (LNG) in more detail with AMN JSC.
The Concept of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is a form of natural gas that mainly contains methane (approximately 95% of its composition). The liquefaction process of LNG is carried out by deep cooling to extremely low temperatures (around -162°C), facilitating storage and transportation to consumption points. Currently, LNG is considered a clean and environmentally friendly energy source and has become popular in many countries around the world.

Liquefied Natural Gas - LNG
Key Features of LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) has outstanding characteristics such as being colorless, odorless, lighter, and easily vaporized into the air. When burned, LNG can produce a flame with a very high temperature (approximately 1880°C). In particular, LNG burns completely without leaving residue, making equipment and machinery operate more safely, reducing wear and tear, requiring less maintenance, and increasing lifespan compared to gasoline and diesel.
LNG is produced by liquefying natural gas at extremely low temperatures, from -120°C to -170°C, where -162°C is considered the standard temperature for optimal removal of impurities and liquefaction of LNG.
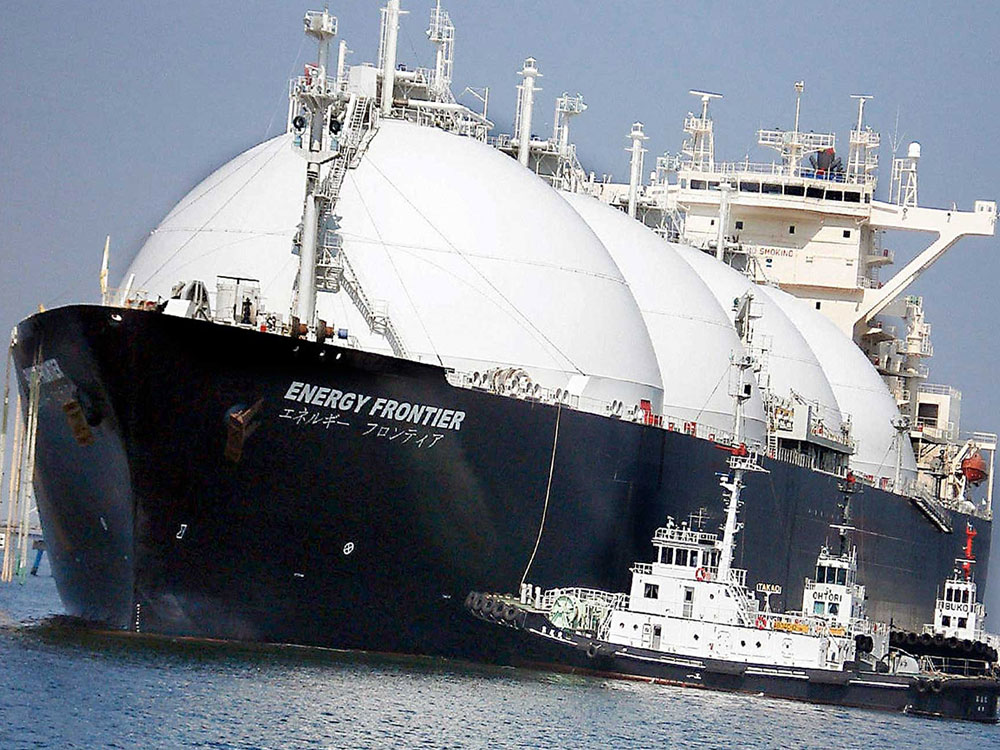

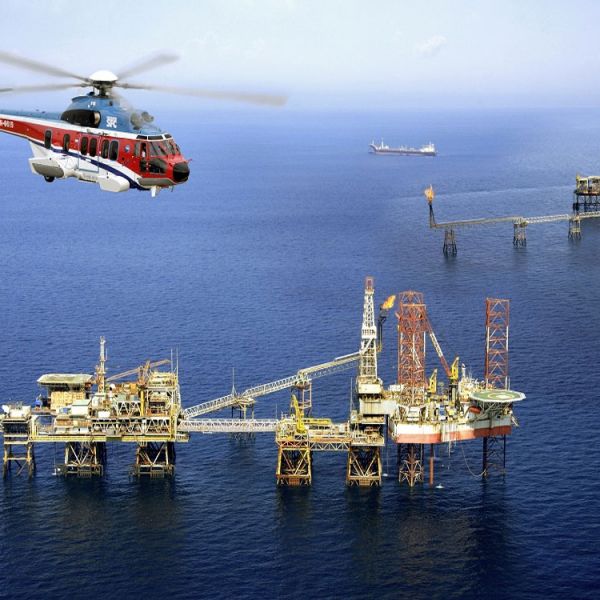
LNG carrier at sea
After liquefaction, LNG has a capacity 2.4 times greater than compressed natural gas CNG. Under standard conditions, LNG occupies only about 1/600th of the total volume of natural gas under standard conditions (1 atm, 15°C). Therefore, LNG is considered a convenient liquefied natural gas product for storage and transportation. This is also the most outstanding advantage of LNG compared to other natural gas products.
How is LNG produced?
To produce LNG, natural gas, after extraction, is first transported to refining plants to remove and process impurities. During this process, non-hydrocarbon compounds are removed, most commonly carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide. After all impurities are completely removed, the natural gas is cooled to -162 degrees Celsius to liquefy it. Finally, the liquefied natural gas (LNG) is pumped into specially designed storage tanks to prevent leakage.
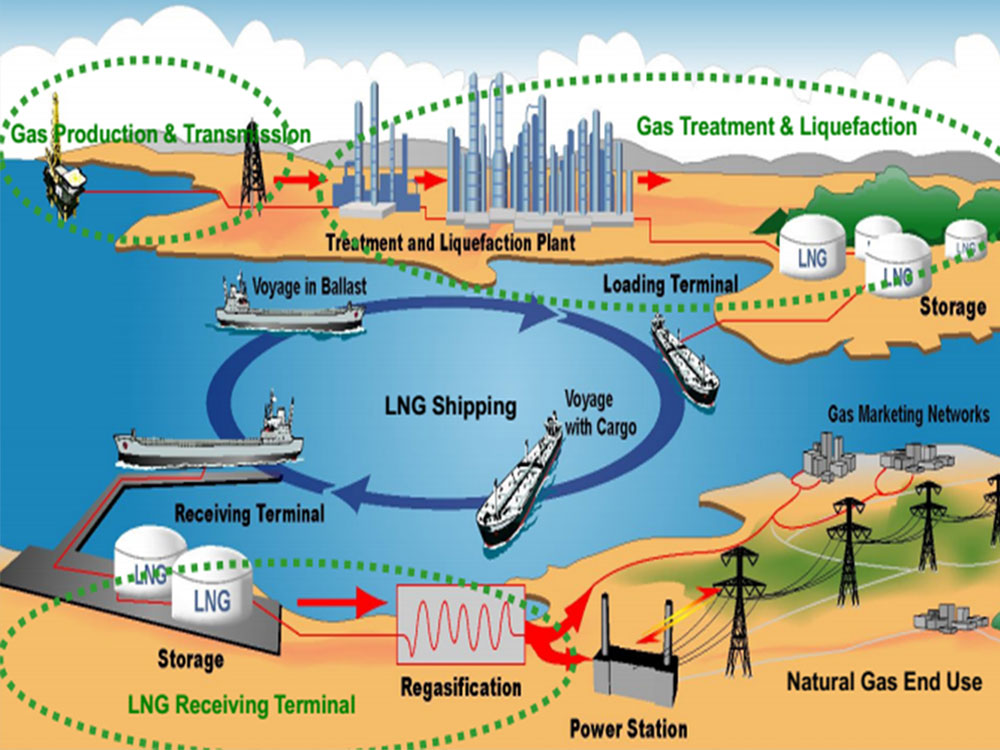
The process of producing liquefied natural gas LNG
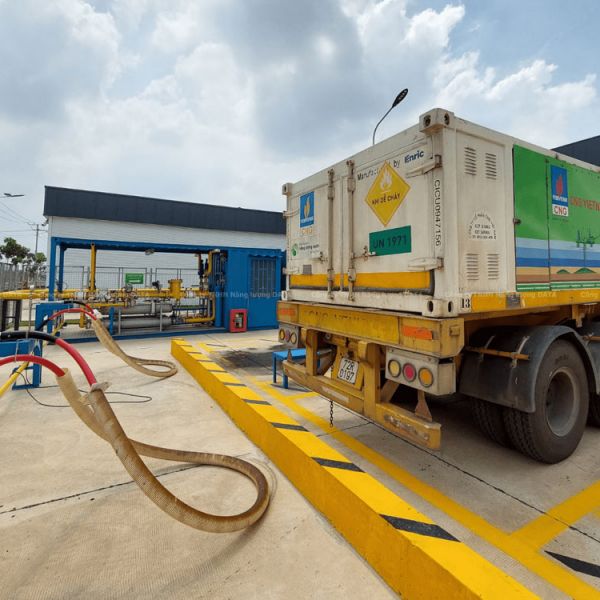
Currently, the primary means of transporting LNG are specialized LNG tankers with capacities ranging from 170,000 m³ to 260,000 m³. Additionally, LNG can also be transported overland by tank trucks and trains with capacities from 2,500 m³ to 12,000 m³. Upon arrival at the point of consumption, the LNG is converted into gas and directly delivered to the consumption site (power plants, residential areas, and industrial zones) via a pipeline system.
Applications of Liquefied Natural Gas LNG
Besides the outstanding advantages mentioned, LNG also offers high economic efficiency and has many practical applications in daily life and industrial production. Compared to diesel and gasoline, LNG has a higher combustion efficiency, not only saving fuel but also protecting the engine, reducing wear and tear, and increasing efficiency. LNG is also considered a safe, non-toxic fuel, easily dispersed in the air, and with a low risk of fire and explosion. Therefore, LNG fires and leaks usually have less serious consequences than gasoline and diesel.
LNG is a highly reliable and very safe natural gas for humans and the environment. It is the cleanest and most economically efficient fossil fuel. According to published documents from several reputable energy management agencies, the world's LNG reserves remain abundant, sufficient to meet humanity's long-term consumption needs. Here are some common applications of LNG in daily life and production that you can refer to:
Using LNG as an alternative fuel to coal in combustion chambers at thermal power plants.
Using LNG as a combustion fuel for heating and drying systems in residential areas and food processing plants.
Using LNG as an alternative fuel to gasoline and diesel in the transportation industry.
Using LNG as a clean energy source for residential areas or households in coastal, island, and remote regions.
Using LNG as fuel in heavy industries such as metallurgy, brick manufacturing, and ceramics production
Is LNG Liquefied Natural Gas Clean Gas?
Liquefied natural gas LNG is a clean energy source with significantly lower emissions than other common fossil fuels such as coal, gasoline, and oil. On average, when the hydrocarbons in LNG burn completely, it releases 40% less greenhouse gas. This is also why many developed countries around the world choose LNG as their primary fuel to reduce their dependence on coal and oil.
In the transportation sector, switching to LNG helps vehicles reduce emissions by 13% to 21% compared to gasoline and diesel. In addition, LNG has a very high combustion efficiency, helping vehicle owners save a lot on fuel costs. Therefore, LNG is truly a clean energy source, effectively reducing emissions and protecting the environment.