LPG, LNG, and CNG are familiar names in the gas and fuel industry. However, you may not yet understand the differences between LPG, LNG, and CNG.
What is LPG?
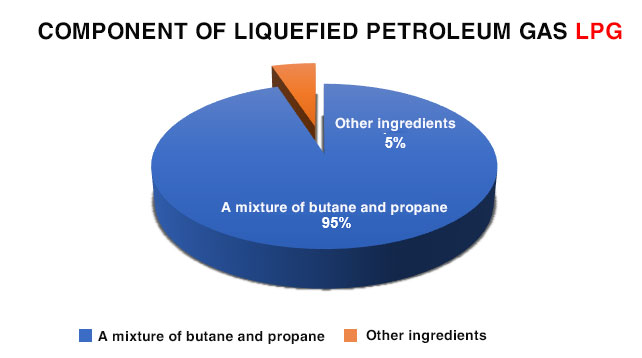
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is a mixture of hydrocarbons consisting mainly of butane (C4H10) and propane (C3H8). The latter components make up at least 95% of the mixture by weight. At normal temperature and pressure, LPG is a gas; it is compressed to a certain pressure or cooled to a certain temperature, causing it to become a liquid.
Applications of LPG
Domestic and Commercial: Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is commonly used in households, hotels, restaurants, and small workshops for cooking, heating, and combustion.
Industrial: LPG is used in industrial production activities such as drying, heating, welding, and combustion. Additionally, LPG is used as a fuel in agricultural production for drying agricultural products, as a fertilizer, etc.
Transportation: LPG is known as an alternative fuel to gasoline and diesel. Therefore, some vehicles are beginning to use LPG to replace traditional gasoline; however, in Vietnam, the use of LPG as a transportation fuel is still quite limited. Studies show that using LPG results in smoother engine operation and lower noise levels. Furthermore, using LPG in taxis can save approximately 25-29% in costs compared to running on gasoline.
LPG is also used in power generation and petrochemicals.
What is CNG?
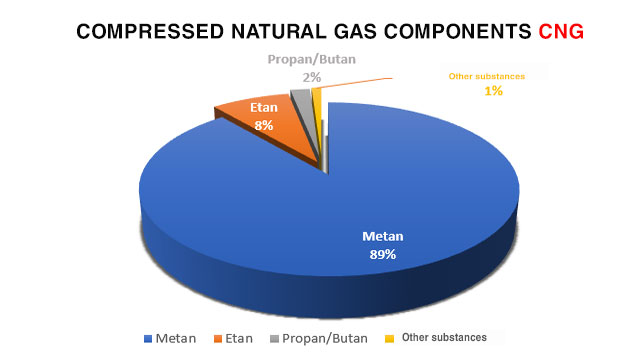
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is natural gas whose main component is methane (up to 95%) compressed at high pressure and transported in specialized vehicles. CNG is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and lighter-than-air natural gas.
Applications of CNG
Transportation: CNG is used as fuel for vehicles such as cars, trucks, and buses. This helps reduce environmentally polluting emissions, save fuel costs, and reduce engine noise.
Industry: In the industrial sector, CNG is used as an alternative energy source to diesel or other petroleum fuels. It is applied in manufacturing processes such as heating, drying, and combustion.
Chemical: CNG is also used in the production of chemical compounds such as ammonia, methanol, and acrylic acid.
Electrical Energy: CNG can be used to generate electricity through gas-fired generator systems. This provides a sustainable energy source and reduces environmental pollution compared to traditional energy sources.
Residential: CNG provides a clean and safe energy source for homes and residential buildings. It can be used for cooking, heating, and water heating.
What is LNG?
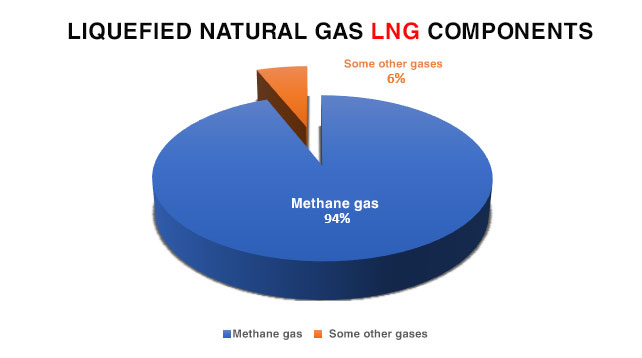
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is a natural gas whose main components are methane (CH4) and a mixture of ethane (C2H6). LNG is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and non-corrosive gas that is cooled to liquid form at a temperature of approximately -162°C. LNG is about 1/1600th the volume of natural gas under standard temperature and pressure conditions, making it relatively easy and safe to transport and store.
Applications of LNG
Domestic: LNG is used to meet human needs such as cooking, baking, heating, dehumidification, etc.
Electrical Energy: LNG can be used to generate electricity through natural gas power plants.
Industrial: LNG is widely used in industrial production with diverse applications such as drying, heating, combustion, and firing.
Commercial: In this sector, LNG is distributed to hospitals, schools, high-rise buildings, restaurants, etc., for heating, air conditioning, dehumidification, or on-site power generation.
Transportation: LNG is used to replace traditional transportation fuels. With good performance and the ability to reduce environmental pollution emissions, LNG is used as fuel for buses, trucks, trains, etc.